
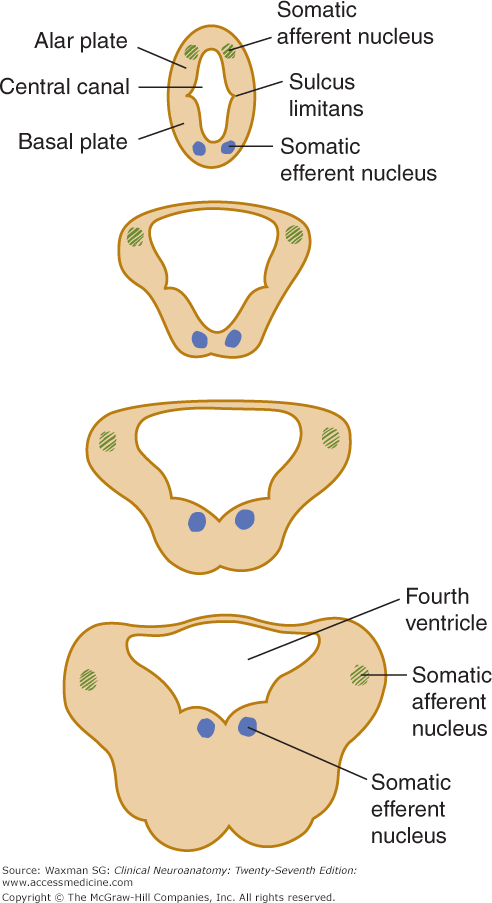
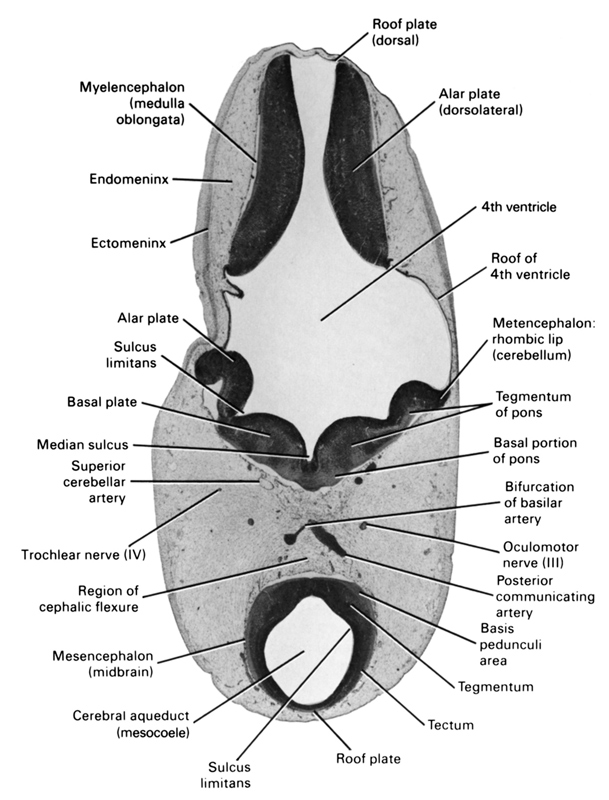
The space into which the cranial part of the neural tube is developing is limited.
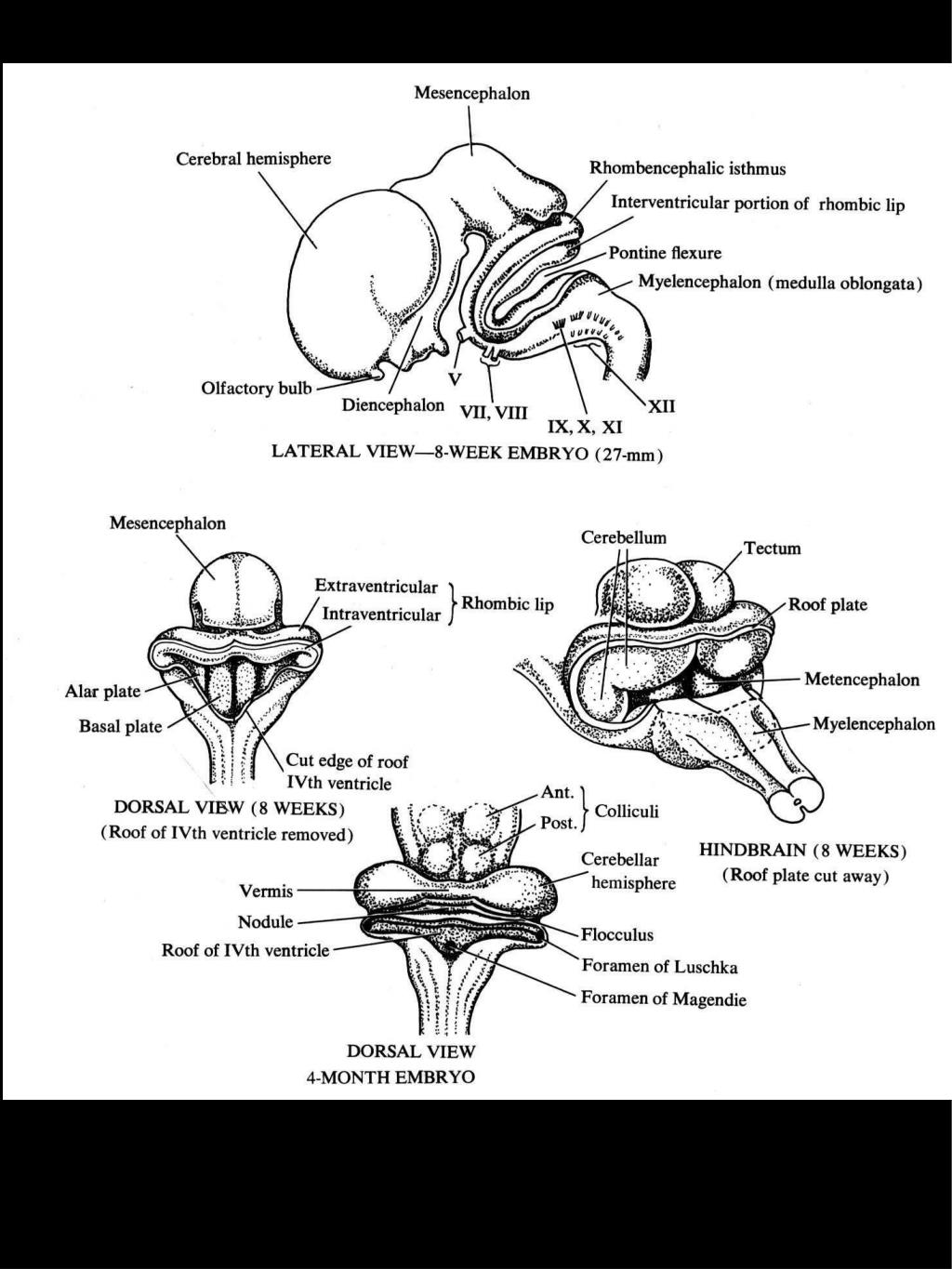
Pages 44 This preview shows page 20 - 38 out of 44 pages. School University of New South Wales Course Title ANAT 2341 Type. Early development of the cns cephalic flexure. At four weeks gestational age in the human embryo the neural tube has developed at the cranial end into three swellings – the primary brain vesicles. Early development of the CNS Cephalic flexure Cervical flexure 3 primary brain. Three flexures form in the part of the embryonic neural tube that develops into the brain.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
